Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) is an important technique we use to fix mistakes that happen during the imaging process in lithography. It involves making changes to the mask to correct any distortions, ensuring that the features printed on silicon closely match the design. OPC is crucial for achieving the right resolution and accuracy, especially when working with smaller and more advanced nodes.
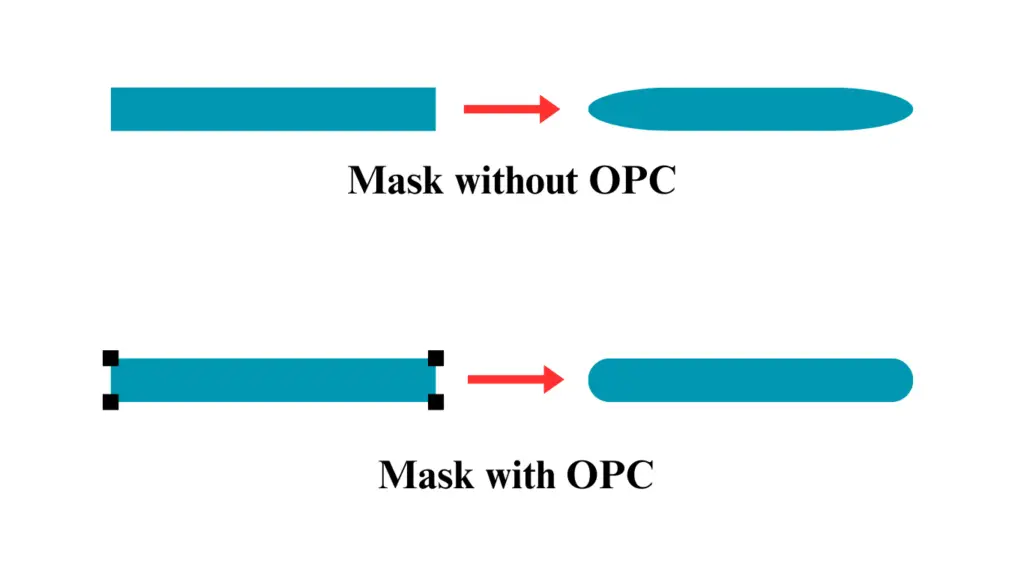
In the above image, the Top mask has no OPC, so its output is coming in a more round shape, while the down mask has OPC at four corners, so the output is coming as near to the input shape. This is how OPC works.
Why do We use Dummy Fill in the Layout Design?
The main idea behind OPC is that we adjust the mask to correct the distortions that occur during the photolithography process. By making these changes, OPC ensures that when the image is printed on silicon, the features match what we designed. This is especially important for creating accurate circuits in small and dense areas at advanced nodes.
Challenges in Advanced Nodes with OPC
In advanced nodes, OPC becomes necessary because small and dense areas on the chip can be difficult to print accurately. As the features compete for space, the imaging system can cause distortions. OPC fixes these issues by adjusting the layout to ensure that the printed features resemble the intended design.
When the line width is very small, especially in advanced nodes, the edges can lose sharpness, causing the printed line to differ from the design. Using techniques like adding dog-ears helps reduce this effect and ensures the printed features stay accurate.
Sharp corners in the layout can become rounded when printed, especially in advanced nodes. We can fix this by adding “mousebites,” which are small indentations in the corners of the layout. This helps keep the corners sharp and closer to the design.
Limitations of OPC
OPC is a powerful tool that helps us tackle challenges in advanced lithography. However, it does come with limitations, such as adding complexity to design rules and potential conflicts with nearby features. Despite these challenges, OPC is essential for creating precise designs in advanced technology nodes. It requires balancing resolution, design rules, and layout adjustments to achieve the best results.
Why OPC needed?
This is where Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) comes in. It’s a technique we use to fix distortions that happen during the lithography process. When light passes through the photomask to print patterns on a wafer, diffraction and other optical effects can cause those patterns to blur or shift, especially when the features are extremely small or placed closely together.
So what do we do? We adjust the mask patterns slightly — we add small shapes or tweak the layout — so that when the light hits the wafer, the final printed result matches what we actually want. It’s kind of like adjusting for distortion in a projector so the image looks right on the screen.
Why should you care about OPC? Because without it, chips wouldn’t function as designed. Features could be too small, too wide, or even missing entirely. As we continue to shrink transistor sizes to follow Moore’s Law, OPC becomes more critical than ever.
In short, OPC helps us bridge the gap between design and reality — making sure the chips we imagine on screen actually come to life on silicon, accurately and reliably.