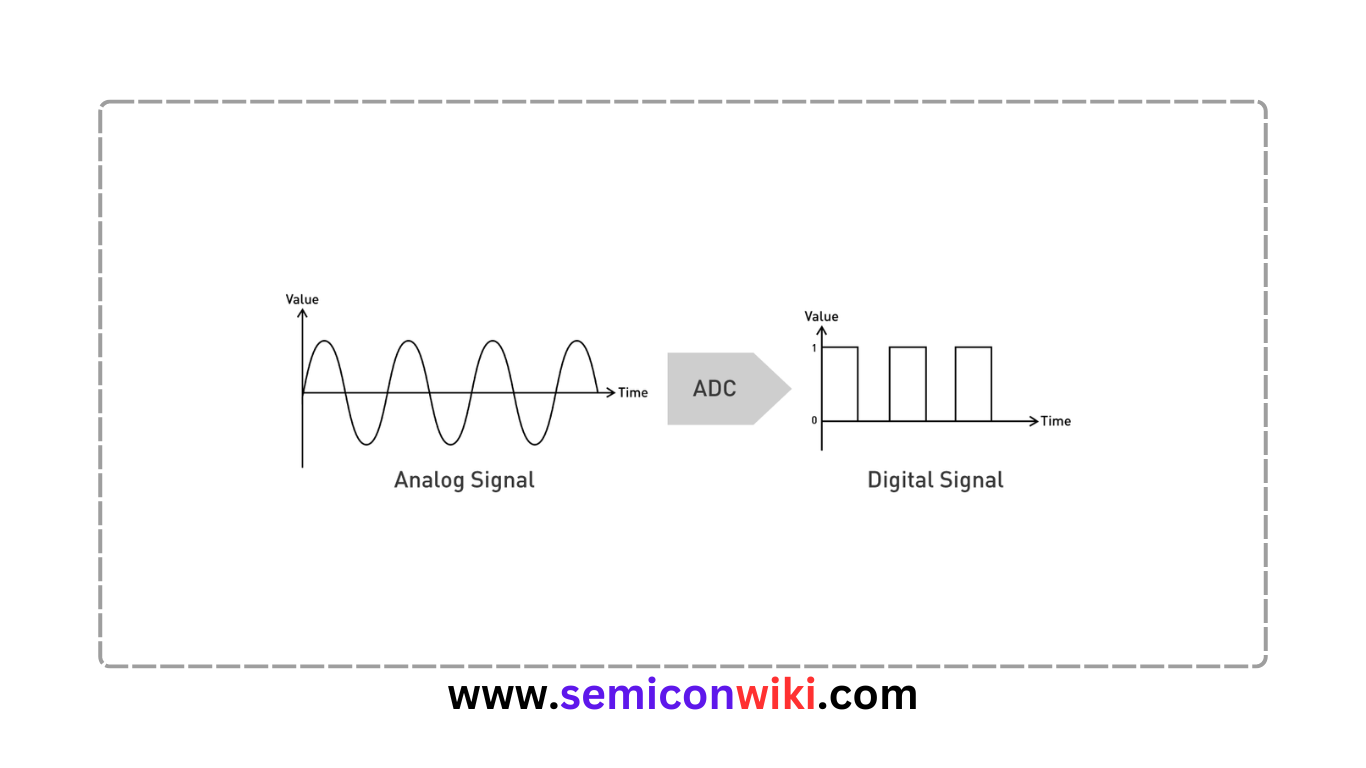
An Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) is an electronic device used to convert analog signals into digital or binary form, consisting of 1s and 0s. The ADC plays a crucial role in systems where digital processing is required, such as microcontrollers and microprocessors.

Sampling
The analog signal is first sampled at regular intervals by the ADC. Sampling is done at an exact frequency determined by the system requirements.
Hold
The sampled analog values are held constant until the next sample is taken. This holding ensures that the value of the sample remains unchanged during the conversion process.
Quantization
The held analog value is then quantized into discrete values. This process converts the continuous analog signal into discrete digital form. The quantization process is crucial for accuracy in digital representation.
Encoding
Finally, the quantized digital values are encoded into binary numbers. This binary representation allows digital devices to process the information.
Features and Types of ADC
Sample Rate: The speed at which an ADC can convert analog signals to digital.
Bit Resolution: The accuracy with which an ADC can convert analog signals to digital.
Applications
ADCs find extensive applications in various fields, including:
- Measurement and control systems
- Industrial instrumentation
- Communication systems
- Sensor-based systems
Types of ADCs
Dual Slope ADC
Uses an integrator circuit to generate a comparison voltage, producing a sawtooth waveform.
Flash ADC
Utilizes a set of comparators to quickly determine the input voltage.
Successive Approximation ADC
Utilizes a binary search algorithm to approximate the input voltage.
Semi-flash ADC
Combines features of flash and successive approximation ADCs.
Sigma-Delta ADC
Converts signals to digital form by oversampling the input signal.
Pipelined ADC
Divides the conversion process into stages, increasing the speed and efficiency of conversion.
Performance Evaluation
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
Reflects the number of bits in a sample without noise.
Bandwidth:
Determines the rate at which the analog source is sampled to produce discrete values.
In conclusion, ADCs are essential in converting analog signals into digital form, enabling digital processing in various applications. They come in different types, each with specific features and performance characteristics suitable for different requirements.
Read also: Innovative Techniques for Pre & Post Layout in VLSI
3-bit Analogue-to-Digital Converter
In the parallel ADC setup, we’re converting an analog input voltage—ranging from 0 to just over 3 volts—into a 3-bit binary output. With 3 bits, you and I can represent 2³, or 8 different digital values. That means the input voltage is compared to eight reference voltage levels, where each level is spaced evenly at one-eighth (V/8) of the full reference voltage.
So, for example, we can detect changes as small as 0.5 volts, which is the difference between the fourth and fifth levels (4/8 of the reference). To make this work, we would need 2³ – 1, or 7 comparators, to generate a binary output ranging from 000 (0) to 111 (7), just like what’s shown in the example.